Ye Mengyuan survived the Asiana Flight 214 plane crash at San Francisco Airport

In 2013, a 16-year-old girl called Ye Mengyuan survived the Asiana Flight 214 plane crash at San Francisco Airport. However, moments after the crash, she was fatally ran over by a responding fire truck arriving at the scene. a tragedy unfolded that would shake the very foundation of aviation safety. Ten years ago, Asiana Airlines Flight 214, a behemoth of the skies, a Boeing 777, was on its final descent to San Francisco International Airport. What was supposed to be the end of a routine transpacific voyage from Seoul turned into a harrowing tale of survival and loss. With 307 souls aboard, the aircraft met with disaster, not from the heavens but upon the familiar ground of the runway. This is their story, etched into the annals of aviation history, a stark reminder of the razor’s edge upon which air travel balances between routine and calamity. Follow Thinkking.vn for more

Prelude to Disaster
As dawn broke on July 6, 2013, Asiana Airlines Flight 214, a Boeing 777-200ER, prepared for its scheduled journey from Incheon International Airport to San Francisco International Airport. This model, renowned for reliability, had been with Asiana Airlines since March 2006, boasting over 37,120 flight hours. Equipped with Pratt and Whitney PW4090 engines, it represented the pinnacle of modern aviation technology and comfort. On that fateful day, the aircraft carried a diverse tapestry of lives—291 passengers from various countries, including 141 Chinese nationals, 77 South Koreans, and 64 Americans, each with their own stories and destinations.
Guiding the aircraft were four seasoned aviators. At the helm was 49-year-old Captain Lee Jeong-min, a veteran with over 12,387 hours of flying, serving his inaugural flight as an instructor. Beside him, Captain Lee Kang-kook, with 9,793 hours in his logbook but only 43 hours on the 777, was undergoing his initial operating experience training. The cockpit was a classroom of experience and instruction, a dynamic that would be scrutinized in the aftermath of the impending catastrophe. These pilots’ backgrounds, a blend of vast experience and new acquaintance with the 777, were a critical element of the incident. As Flight 214 approached its destination, none aboard could foresee that their journey would become a pivotal case study in aviation safety, leaving an indelible imprint on the history of civil aviation.
The Final Approach
On the clear morning of July 6, 2013, Asiana Airlines Flight 214, carrying 307 souls, approached the end of its transpacific voyage. The descent into San Francisco was routine until the final moments. The Boeing 777-200ER, under the control of a crew with a mix of vast and limited experience on the type, began its approach. The usual hum of the engines and the calm commands in the cockpit belied the impending disaster.
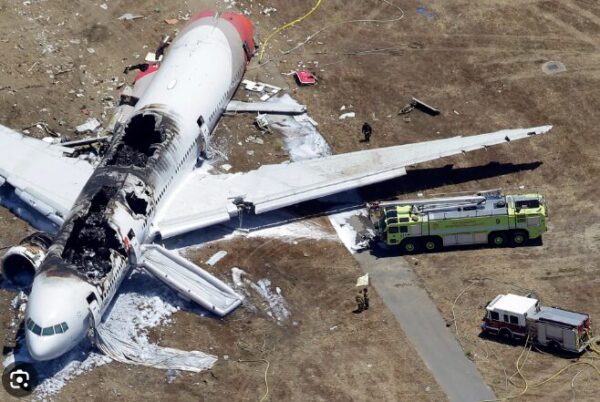
The timeline of the descent was disrupted as the aircraft, instead of gliding smoothly onto the runway, came in too low and too slow. The pilots’ attempts to correct the trajectory came too late. At 11:28 AM local time, the 777’s landing gear and then its tail struck the seawall just short of Runway 28L. The impact was devastating—the rear of the aircraft severed, sending a shockwave through the cabin and hurling four flight attendants, still strapped to their seats, onto the runway.
In the chaotic aftermath, the fuselage twisted and skidded before coming to rest on the tarmac, flames and smoke billowing as the aircraft began to break apart. Inside, passengers screamed and braced, as the realization of their plight set in. Outside, emergency crews raced against time, converging on the scene to combat the fire and rescue the survivors. Amidst the mangled debris and the heroics of first responders, the moment of impact marked not just a tragic episode in aviation history but also a starting point for profound safety lessons that would resonate in the years to follow.

Aftermath and Rescue Operations
In the tense moments following the crash of Asiana Airlines Flight 214, the emergency response was swift and decisive. San Francisco International Airport’s rescue personnel sprang into action, a testament to their rigorous training and preparedness. Firefighters and medical teams were dispatched within seconds, their sirens piercing the calm as they converged on the crippled jetliner. Their primary objective was to douse the flames engulfing the aircraft and prevent a potential inferno.
Simultaneously, the evacuation procedures were initiated. Flight attendants, some injured, channeled their training into action, shouting commands and directing dazed passengers to the emergency exits. Slides deployed, and passengers, urged by the crew, scrambled onto the wings and slid down, racing away from the burning wreckage. Amidst the chaos, acts of heroism surfaced—passengers helping one another, shielding the vulnerable, and retrieving the injured, showcasing the best of humanity in the direst of circumstances.
Survivor stories emerged, painting a vivid picture of the evacuation. Personal accounts spoke of the terrifying descent, the jolt of the impact, and the fear-laden rush to escape the aircraft. However, intertwined with the fear were narratives of resilience and courage. There were tales of strangers binding together, of passengers comforting children, and of the injured insisting others be attended to first. The collective efforts of the crew, the first responders, and the passengers themselves led to the successful evacuation of nearly everyone on board, turning a potential catastrophe into a story of survival and bravery that resonated worldwide.
Investigating the Crash
The National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) conducted a thorough investigation into the crash of Asiana Airlines Flight 214, meticulously analyzing the flight data, cockpit voice recordings, and the wreckage itself. The findings revealed a multifaceted picture of human error exacerbated by complex automation systems.
The NTSB pointed to the flight crew’s mismanagement of the airplane’s descent as the primary cause. The pilots’ reliance on the autothrottle system, which they mistakenly believed would maintain the correct airspeed for landing, was a critical error. The investigation highlighted a lack of understanding and communication among the crew members regarding the operation of the airliner’s automation systems. Furthermore, the NTSB noted that Boeing’s documentation and training did not adequately cover the nuances of the autothrottle and autopilot flight director systems, especially concerning their behavior when connected in certain ways during landing approaches.
In response to the NTSB’s findings, Asiana Airlines took steps to overhaul its pilot training program. The airline implemented more rigorous training focused on manual flying skills, automation policies, and crew resource management to enhance cockpit communication and decision-making. Simulators were used to recreate the crash scenario, allowing pilots to practice recovering from similar situations. Additionally, Asiana reviewed and revised its safety procedures to improve the response to in-flight anomalies and emergencies. These measures aimed to address the deficiencies identified by the investigation and to prevent similar incidents from occurring in the future.
The Legacy of Flight 214
The crash of Asiana Airlines Flight 214 had a profound impact on aviation safety, prompting reforms and leading to changes in procedures for the Boeing 777, as well as broader enhancements in global aviation safety practices.
In the aftermath of the crash, Boeing made revisions to its 777 flight manuals and training, specifically addressing the complexities of its autothrottle system to ensure pilots had a clearer understanding of its operation during all phases of flight. The event propelled a re-examination of cockpit automation and human factors, leading to more robust training that emphasizes manual flying skills and better management of automated systems.
Globally, airlines and aviation authorities took heed of the lessons learned from Flight 214. There was an industry-wide push to improve pilot training programs, particularly in aspects of crew resource management and automation reliance. The incident also sparked discussions on enhancing the design of cockpit systems to make them more intuitive and less prone to misinterpretation by flight crews.
The legacy of Flight 214 also encompasses the solemn remembrance of the lives lost and the many more that were forever changed. Tributes to the victims were held, both immediately following the crash and on subsequent anniversaries. Monuments and memorials were established to honor their memory and to serve as a reminder of the importance of continuing to strive for safety in aviation.
For survivors, the psychological and physical scars endured have necessitated ongoing support. Counseling services, support groups, and community outreach programs were established to assist those affected. These services provide a network of care and support, helping survivors cope with the trauma and rebuild their lives.
Flight 214’s legacy is a complex tapestry of tragedy, resilience, reform, and learning. It stands as a somber testament to the imperative of continuous improvement in aviation safety and the enduring human spirit in the face of adversity.
FAQs
1: What caused the crash of Asiana Flight 214?
The NTSB concluded that the accident was caused by the flight crew’s mismanagement of the airplane’s final approach, along with contributory factors including deficiencies in Boeing’s documentation and in Asiana Airlines’ pilot training.
2: How did the crash affect Boeing 777’s safety reputation?
Despite the Asiana Flight 214 crash, the Boeing 777 has maintained a reputation for safety. This was its first fatal accident since entering service in 1995, leading to increased scrutiny and improvements in safety protocols.
3: What changes were made in pilot training after the crash?
Asiana Airlines overhauled its pilot training program, incorporating more comprehensive simulations and checks to better prepare pilots for handling complex flight control systems and emergency situations.
4: How are victims and survivors commemorated?
Memorials have been held to honor the victims, and support networks were established for the survivors. The aviation industry continues to use the incident as a case study for safety training and awareness.