Viral Exanthem Rash: Diagnosis, Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
Welcome to Thinkking.vn, where we delve deep into various health topics to provide you with accurate and comprehensive information. Today, we’re shedding light on a prevalent skin condition – “Viral Exanthem Rash: Diagnosis, Symptoms, Causes & Treatment” Read on to understand its causes, symptoms, and effective treatments, ensuring you’re well-informed about this common ailment.
I. Introduction to Viral Exanthem Rash
The term “Viral Exanthem Rash” refers to a specific type of skin reaction that stems from a viral infection. This rash is characterized by its widespread appearance on the body, often manifesting as spots, bumps, or blotches. Delving deeper into the terminology, the word “exanthem” is a medical term used to describe a widespread rash that is usually accompanied by systemic symptoms, such as fever or malaise. In the context of the Viral Exanthem Rash, it is crucial to understand that this rash is not just a superficial skin issue but often an indication of an underlying viral infection affecting the body’s system. Whether you’ve come across this term in medical literature or heard it in passing, gaining a comprehensive understanding of Viral Exanthem can help in recognizing its signs and implications.
II. Causes of Viral Exanthem Rash
The occurrence of the “Viral Exanthem Rash” is primarily attributed to certain viral infections, but the exact mechanism through which these rashes manifest can vary. There are three primary ways through which a virus can lead to the development of a Viral Exanthem Rash:
- Immune Response: One of the most common reasons for the appearance of Viral Exanthem Rash is the body’s immune response to a viral infection. As the body detects and fights off the virus, it can sometimes cause an inflammatory reaction on the skin, resulting in the rash.
- Damage by the Organism: Some viruses directly harm the skin cells, leading to the characteristic symptoms of Viral Exanthem Rash.
- Toxin-Induced Reactions: Certain viruses produce toxins as part of their lifecycle. The body’s reaction to these toxins can manifest as the Viral Exanthem Rash.
While many viruses can cause this rash, some are more commonly associated with it than others. Notable examples of viruses that frequently result in exanthem rash include Chickenpox (caused by the varicella-zoster virus), COVID-19 (caused by the coronavirus), and Fifth disease (caused by parvovirus B19), among others.
However, it’s crucial to note that other viruses can also potentially lead to Viral Exanthem Rash, even if they aren’t as commonly recognized for this symptom.
Beyond viral causes, exanthems can also arise due to bacterial infections. For instance, certain strains of staphylococcus and streptococcus bacteria produce toxins that can cause skin reactions resembling the Viral Exanthem. Additionally, drug reactions, especially to antibiotics or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, can induce exanthems. Some connective tissue diseases, characterized by inflammation of the skin and other organs, may also present with a rash similar to the Viral Exanthem.
III. Symptoms of Viral Exanthem Rash
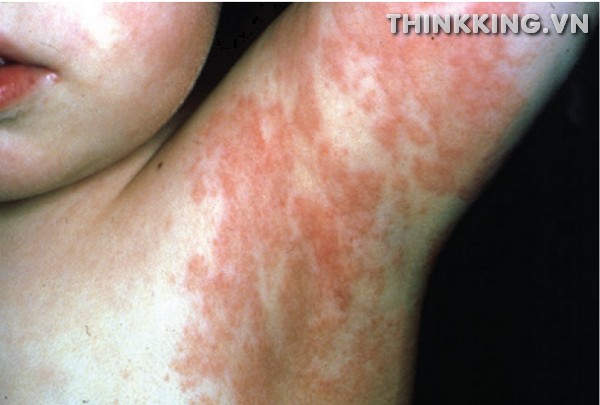
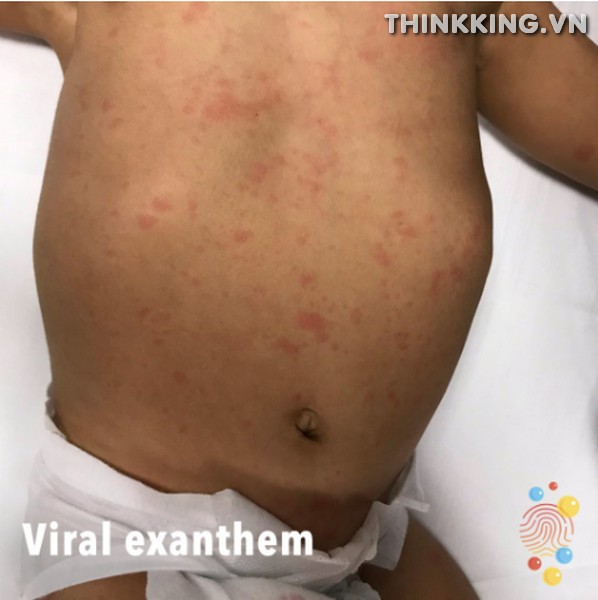
Recognizing the symptoms of “Viral Exanthem Rash” is crucial for early detection and appropriate management. The primary hallmark of this condition is the appearance of a distinctive rash on the skin.
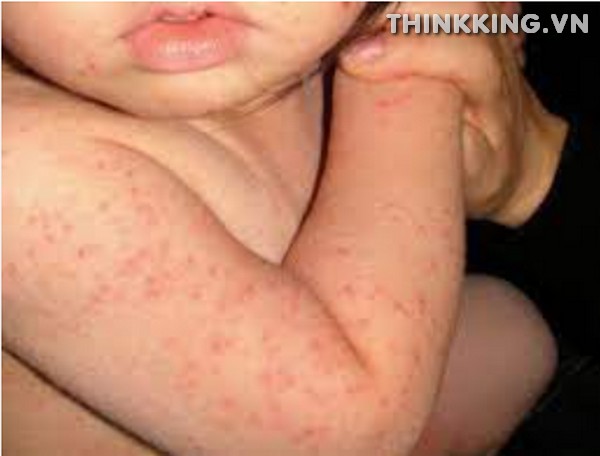
- Description of the Rash: The Viral Exanthem Rash typically manifests as spots, bumps, or blotches on the skin. These can vary in size and intensity, but they are often red or pink in color and can sometimes be raised or itchy. The texture of the rash can be slightly rough to the touch, and the affected areas might feel warm.
- Typical Progression: The onset of the Viral Exanthem Rash often begins on more centralized parts of the body, such as the face or trunk. As the condition progresses, the rash can spread outwards, extending to the limbs and other parts of the body. This spreading pattern is a distinguishing feature of Viral Exanthem Rash and can help in differentiating it from other types of skin reactions.
- Associated Viral Symptoms: In addition to the skin manifestations, Viral Exanthem Rash is often accompanied by other systemic symptoms indicative of a viral infection. Patients might experience fever, fatigue, malaise, or muscle aches. In some cases, there might also be respiratory symptoms like a cough or sore throat, or gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea or diarrhea. These associated symptoms provide further context to the presence of the Viral Exanthem Rash and underline its connection to an underlying viral infection.
IV. Contagious Nature of Viral Exanthem Rash
One of the most pertinent concerns surrounding the “Viral Exanthem Rash” is its contagious nature. As the name suggests, this rash is rooted in a viral infection, and like many viral conditions, it can be transmitted from one person to another.
- Understanding the Spread: The Viral Exanthem Rash, in itself, is a manifestation of an underlying viral infection. When an infected individual comes into close contact with others, there’s a risk of the virus being transmitted. This can happen through direct skin-to-skin contact, sharing personal items, or even through respiratory droplets if the causative virus is airborne. The presence of the Viral Exanthem often indicates an active viral phase, making the individual more likely to spread the condition.
- Consultation with Healthcare Provider: Given the contagious nature of Viral Exanthem , it’s of utmost importance to consult a healthcare provider upon noticing the symptoms. They can offer guidance on when it’s safe to return to daily activities such as work, school, or social gatherings. Following medical advice not only ensures the well-being of the affected individual but also helps in preventing the further spread of the virus.
- Special Precautions: Certain groups of individuals, like pregnant women and those with compromised immune systems, are at a heightened risk when exposed to viruses. The implications of catching a viral infection can be more severe for them. For instance, some viruses can lead to complications during pregnancy or might hit harder in someone with a weakened immune system. Therefore, individuals displaying the Viral Exanthem Rash should exercise extreme caution around these vulnerable groups. It’s always recommended to maintain distance, practice good hygiene, and communicate about the presence of the rash to those around, allowing them to take necessary precautions.
In summary, understanding the contagious nature of Viral Exanthem and taking responsible steps can prevent its widespread transmission and protect the community at large.
V. Diagnosis of Exanthems
Diagnosing conditions like the “Viral Exanthem ” is a meticulous process that hinges on a combination of clinical observations and specific tests. Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial to ensure appropriate treatment and prevent further complications.
- Distinct Patterns and Prodromal Symptoms: One of the primary tools for diagnosing Viral Exanthem is the recognition of its characteristic appearance and progression. The rash often presents in distinct patterns, such as spots, blotches, or bumps on the skin. Furthermore, before the appearance of the rash, patients might exhibit prodromal symptoms — these are early signs that precede the more obvious and characteristic symptoms of the condition. For the Viral Exanthem , prodromal symptoms might include fever, fatigue, or general malaise. Recognizing these signs and patterns can provide healthcare providers with crucial clues about the underlying cause of the rash.
- Recommended Clinical Tests: While visual examination and patient history play a significant role, they are often supplemented with specific clinical tests to confirm the diagnosis of Viral Exanthem. Some of the recommended tests include:
- Viral Swab: This involves taking a sample from the patient, usually from the throat, nose, or the site of the rash, to test for the presence of a specific virus.
- Blood Tests: Blood samples can provide a wealth of information. They can be tested for the presence of certain antibodies, indicating a past or current viral infection. Additionally, other markers in the blood can give insights into the patient’s overall health and the nature of the rash.
- Genotyping: In some cases, it might be beneficial to determine the specific strain or type of a virus. Genotyping can provide this information, helping healthcare providers tailor their treatment approach.
In conclusion, diagnosing Viral Exanthem Rash is a multi-step process that combines clinical expertise with advanced testing. Ensuring an accurate diagnosis is the cornerstone to effective treatment and better patient outcomes.
VI. Treatment for Exanthems
Addressing conditions like the “Viral Exanthem Rash” requires a comprehensive treatment approach, taking into account the root cause and the presenting symptoms. Effective management not only alleviates discomfort but also minimizes the risk of complications.
- Treatment Depending on the Cause: The primary step in treating Viral Exanthem Rash is identifying its underlying cause. Since this rash can be a manifestation of various viral infections, pinpointing the specific virus is essential. For instance, the treatment approach for a rash resulting from the varicella-zoster virus (chickenpox) will differ from one caused by the coronavirus (COVID-19). Thus, a tailored treatment plan is crucial for addressing the root of the problem effectively.
- Symptomatic Treatments: While addressing the cause is paramount, alleviating the discomforting symptoms associated with the Viral Exanthem Rash is equally vital. Some of the common symptomatic treatments include:
- Paracetamol: This over-the-counter medication is frequently recommended to reduce fever and alleviate pain. It can help in bringing down high temperatures and making the patient feel more comfortable.
- Moisturizing Emollients: The itchiness accompanying the Viral Exanthem Rash can be quite bothersome. Moisturizing emollients can be applied to the affected areas to soothe the skin and reduce itchiness. These moisturizers form a protective layer, preventing further dryness and irritation.
- Recommendations for Managing the Rash and Associated Symptoms: Apart from medical treatments, certain practices can be beneficial in managing the Viral Exanthem Rash:
- Avoid Scratching: Scratching the rash can lead to further inflammation and even potential infections. It’s advisable to keep the nails short and clean to minimize damage.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can aid in skin health, potentially reducing the severity of the rash.
- Loose Clothing: Wearing breathable, loose-fitting clothes can prevent further irritation of the affected areas.
In essence, the treatment for Viral Exanthem involves a combination of addressing the underlying cause and managing the symptoms. With the right approach and consistent care, patients can expect a gradual improvement in their condition.
FAQs
- What causes viral exanthem rash?
- A viral exanthem rash can be caused by a virus in several ways:
- The rash can be the body’s immune response to the virus.
- It can result from damage to the skin by the virus.
- It might be a reaction to a toxin the virus produces.
- Common viruses that cause exanthem rash include Chickenpox, COVID-19, Fifth disease, Hand, foot and mouth disease, Measles, Roseola, Rubella, among others.
- A viral exanthem rash can be caused by a virus in several ways:
- What are the symptoms of a viral exanthem rash?
- A viral exanthem rash typically manifests as spots, bumps, or blotches on the skin. They can appear anywhere on the body but frequently start on the face or trunk before spreading. The rash may or may not be itchy. Additionally, individuals might experience other viral symptoms like fever, fatigue, and malaise.
- Is a viral exanthem rash contagious?
- Yes, the viruses that cause viral exanthem rashes are contagious. They can spread easily from person to person, which is why it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider about when it’s safe to resume daily activities and be around others.
- What is an exanthem?
- An exanthem refers to a widespread rash often accompanied by systemic symptoms such as fever, malaise, and headache. It is typically caused by infectious conditions like viruses and can represent a reaction to a toxin produced by the organism, direct damage to the skin by the organism, or an immune response.
- What causes exanthems?
- Exanthems are commonly caused by specific viral infections like Chickenpox, Measles, Rubella, and Roseola, among others. They can also result from bacterial infections like Staphylococcal or Streptococcal toxin infections, other specific infections like Mycoplasma pneumonia, and Rickettsial diseases. Additionally, drugs, especially antibiotics and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications, can cause exanthems.
- What are the signs and symptoms of exanthems?
- Exanthems often present as spots or blotches that may or may not be itchy. The rash is typically widespread and may be more concentrated on the trunk than the limbs. Before the rash’s appearance, individuals might experience symptoms like fever, malaise, headache, loss of appetite, abdominal pain, irritability, and muscle aches.
- Diagnosis of exanthems
- Many exanthems have unique patterns of rashes and prodromal (pre-rash) symptoms that allow for clinical diagnosis. In uncertain cases, tests like viral swabs for viral culture, blood tests for serology, and genotyping can be conducted.
- What is the treatment for exanthems?
- The treatment for exanthems largely depends on the cause. If the exanthem is due to a virus, antiviral medications might be prescribed. Symptomatic treatments, such as paracetamol for fever or moisturizing emollients for itchiness, can be used to alleviate discomfort. In cases where exanthems are caused by bacterial infections, antibiotics might be necessary. Proper diagnosis is crucial to ensure effective treatment.
| “Please note that all information presented in this article has been obtained from a variety of sources, including wikipedia.org and several other newspapers. Although we have tried our best to verify all information, we cannot guarantee that everything mentioned is accurate and 100% verified. Therefore, we recommend caution when referencing this article or using it as a source in your own research or report.” |